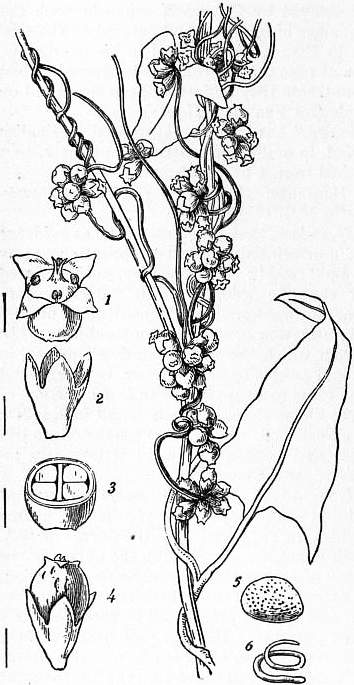
Dodder (Frisian dodd, a bunch; Dutch dot, ravelled thread), the popular name of the annual, leafless, twining, parasitic plants forming the genus Cuscuta, formerly regarded as representing a distinct natural order Cuscutaceae, but now generally ranked as a tribe of the natural order Convolvulaceae. The genus contains nearly 100 species and is widely distributed in the temperate and warmer parts of the earth. The slender thread-like stem is white, yellow, or red in colour, bears no leaves, and attaches itself by suckers to the stem or leaves of some other plant round which it twines and from which it derives its nourishment. It bears clusters of small flowers with a four- or five-toothed calyx, a cup-shaped corolla with four or five stamens inserted on its tube, and sometimes a ring of scales below the stamens; the two-celled ovary becomes when ripe a capsule splitting by a ring just above the base. The seeds are angular and contain a thread-like spirally coiled embryo which bears no cotyledons. On coming in contact with the living stem of some other plant the seedling dodder throws out a sucker, by which it attaches itself and begins to absorb the sap of its foster-parent; it then soon ceases to have any connexion with the ground. As it grows, it throws out fresh suckers, establishing itself firmly on the host-plant (fig. 2). After making a few turns round one stem the dodder finds its way to another, and thus it continues twining and branching till it resembles “fine, closely-tangled, wet catgut.” The injury done to flax, clover, hop and bean crops by species of dodder is often very great. C. europaea, the greater dodder (fig. 1) is found parasitic on nettles, thistles, vetches and the hop; C. Epilinum, on flax; C. Epithymum, on furze, ling and thyme. C. Trifolii, the Clover Dodder, is perhaps a subspecies of the last mentioned.
 |
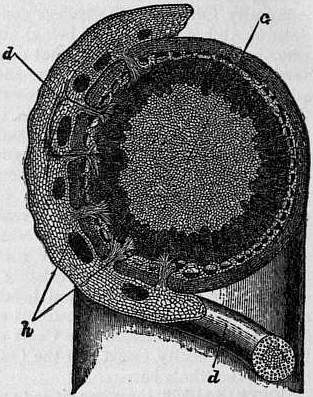 |
| Fig. 1.—Cuscuta europaea, Dodder. | Fig. 2.—Cuscuta glomerata. Section through union between parasite and host. |
1. Flower removed from 2, Calyx. 3. Ovary cut across. 4. Fruit enveloped by a persistent corolla. 5. Seed. 6. Embryo. 1-6 enlarged. |
c, stem of host. d, stem of Cuscuta. h, haustoria. (After Dodel-Port.) |


