Coumarones or Benzofurfuranes, organic compounds containing the ring system 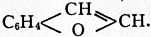 This ring system may be synthesized in many different ways, the chief methods employed being as follows: by the action of hot alcoholic potash on α-bromcoumarin (R. Fittig, Ann., 1883, 216, p. 162),
This ring system may be synthesized in many different ways, the chief methods employed being as follows: by the action of hot alcoholic potash on α-bromcoumarin (R. Fittig, Ann., 1883, 216, p. 162),
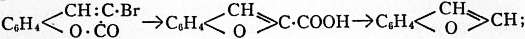 |
from sodium salts of phenols and α-chloracetoacetic ester (A. Hantzsch, Ber., 1886, 19, p. 1292),
 |
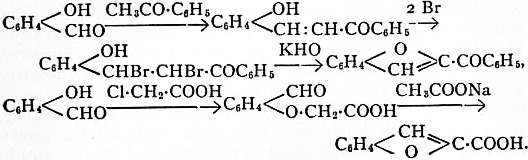
or from ortho-oxyaldehydes by condensation with ketones (S. Kostanecki and J. Tambor, Ber., 1896, 29, p. 237), or with chloracetic acid (A. Rossing, Ber., 1884, 17, p. 3000),
 |
The parent substance coumarone, C8H6O, is also obtained by heating ω-chlor-ortho-oxystyrol with concentrated potash solution (G. Komppa, Ber., 1893, 26. p. 2971),
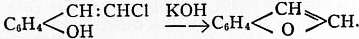 |
It is a colourless liquid which boils at 171-172° C. and is readily volatile in steam, but is insoluble in water and in potash solution. Concentrated acids convert it into a resin. When heated with sodium and absolute alcohol, it is converted into hydrocoumarone, C8H8O, and ethyl phenol.


